The Fed Finally Seeing The Magnitude Of The Mess It Created
Sept 23, 2022 18:33:08 GMT -5
Post by schwartzie on Sept 23, 2022 18:33:08 GMT -5
The Fed Is Finally Seeing The Magnitude Of The Mess It Created
FRIDAY, SEP 23, 2022 - 08:45 AM
Authored by Ryan McMaken via The Mises Institute,
When asked about price inflation in his Sunday interview with 60 Minutes, President Biden claimed that inflation "was up just an inch...hardly at all." Biden continued the dishonest tactic of focuses on month-to-month price inflation growth as a means of obscuring the 40-year highs in year-over-year inflation. This strategy may yet work to placate the most ignorant voters, but people who are paying attention know that price inflation continues to soar.
Thus, while Biden may be pretending that it's all no big deal, the Federal Reserve knows it better do something about price inflation which even the Fed now admits shows no signs of even moderating.
Another 75 Basis Points
On Wednesday, the Fed's Federal Open Market Committee announced that it will again raise the federal funds rate by 75 basis points. According to the FOMC's press release:
Inflation remains elevated, reflecting supply and demand imbalances related to the pandemic, higher food and energy prices, and broader price pressures. ...
The Committee decided to raise the target range for the federal funds rate to 3 to 3-1/4 percent and anticipates that ongoing increases in the target range will be appropriate. In addition, the Committee will continue reducing its holdings of Treasury securities and agency debt and agency mortgage-backed securities, as described in the Plans for Reducing the Size of the Federal Reserve's Balance Sheet that were issued in May. The Committee is strongly committed to returning inflation to its 2 percent objective.
This is, by far, the most hawkish announcement yet out of the Powell Fed and no doubt reflects the fact the Fed has finally come to terms with the fact that inflation is not transitory—as the Fed long insisted—and is now impossible to deny. Last month, CPI inflation rose 8.2 percent, year over year, marking six months of year-over-year price inflation rates over 8 percent and near 40-year highs.
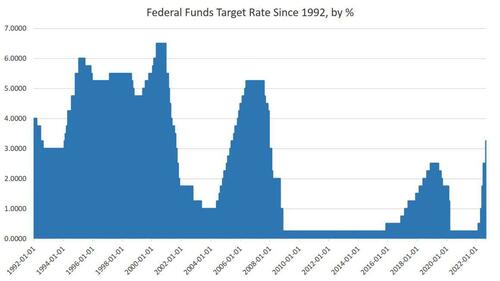
Moreover, in its summary of economic projections, many FOMC committee members said they expected the target policy rate to reach or exceed 4.25 percent this year, and exceed 4.5 percent in 2023. Projections of economic conditions, however, continued to be relatively rosy with the report suggesting that GDP growth will stay above zero for the foreseeable future while unemployment maxes out at only 5 percent.
In spite of two quarters in a row of shrinking GDP over the past year, and in spite of many indicators of brewing recession—such as falling home prices and an inverting yield curve—the committee is still clinging to the idea that the Fed can steer a "soft landing" in which inflation will be reined in with no more than some moderate slowing in economic growth.
Although the recent hikes in the target fed funds rate suggest an increasingly hawkish position, the Fed nonetheless continues to take only the most tepid steps when it comes to reducing the size of the Fed's portfolio. Such a move would directly reduce the money supply by reversing QE, and it would also reduce asset prices by producing a small deluge of government bonds and mortgage-backed securities flowing back into the market.
While the Fed is allowing some government bonds to continue to roll off the portfolio, we shouldn't expect any drastic moves here. It's been nearly four months since the Fed announced plans to reduce the portfolio, yet the actual reduction continues to be miniscule. Moreover, in Powell's press conference on Wednesday, when asked about selling off the Fed's mortgage-backed securities, Powell responded "It's something I think we will turn to, but that time — the time for turning to it has not come ... It's not close."
Even now, after immense and rapid price inflation over the past two years, the Fed is still too afraid of fragility in the housing market to put much of its $2 trillion MBS portfolio back into the private sector.
This sends a mixed message as to how much the Fed is really committed to reducing price inflation, but it's clear Powell was trying to project a hawkish tone on Wednesday overall.
Powell spoke of "significantly reducing the size of our balance sheet" and also emphasized that ending the current bout of inflation will require pain in the form of job losses. He also emphasized that there is no short-term solution, strongly implying that the current effort to end inflation could possibly take years.
Powell expressed fears that price inflation will become much harder to address once the population comes to expect inflation as routine. He also noted that price inflation in housing "is going to remain high for some time." Powell then reiterated that there is no way to "wish away" inflation, but that the only way he sees the Fed can do something about inflation is by "slow[ing] the economy." (See 1:35:00 here.)
The question remains, however, as to whether or not the Fed and the federal government can politically tolerate a sizable period of rising interest rates and a decline in the monetary growth rate.
A decline in the monetary growth rate is trouble because it points to recession. Our bubble economy is now so addicted to easy money, that even a slowing in monetary expansion can send the economy's many zombie companies into a tailspin. Rising rates are a problem because they can lead to sizable increase in the federal government's debt-service payments. This could lead to a fiscal crisis without cuts to popular government spending programs. Virtually no one in Washington wants that.
Some key warning signs are already flashing "recession," such as the inverting yield curve. For example, the 10-year yield minus the 2-year yield has been negative since July, and at the most negative level since the early 1980s.
FRIDAY, SEP 23, 2022 - 08:45 AM
Authored by Ryan McMaken via The Mises Institute,
When asked about price inflation in his Sunday interview with 60 Minutes, President Biden claimed that inflation "was up just an inch...hardly at all." Biden continued the dishonest tactic of focuses on month-to-month price inflation growth as a means of obscuring the 40-year highs in year-over-year inflation. This strategy may yet work to placate the most ignorant voters, but people who are paying attention know that price inflation continues to soar.
Thus, while Biden may be pretending that it's all no big deal, the Federal Reserve knows it better do something about price inflation which even the Fed now admits shows no signs of even moderating.
Another 75 Basis Points
On Wednesday, the Fed's Federal Open Market Committee announced that it will again raise the federal funds rate by 75 basis points. According to the FOMC's press release:
Inflation remains elevated, reflecting supply and demand imbalances related to the pandemic, higher food and energy prices, and broader price pressures. ...
The Committee decided to raise the target range for the federal funds rate to 3 to 3-1/4 percent and anticipates that ongoing increases in the target range will be appropriate. In addition, the Committee will continue reducing its holdings of Treasury securities and agency debt and agency mortgage-backed securities, as described in the Plans for Reducing the Size of the Federal Reserve's Balance Sheet that were issued in May. The Committee is strongly committed to returning inflation to its 2 percent objective.
This is, by far, the most hawkish announcement yet out of the Powell Fed and no doubt reflects the fact the Fed has finally come to terms with the fact that inflation is not transitory—as the Fed long insisted—and is now impossible to deny. Last month, CPI inflation rose 8.2 percent, year over year, marking six months of year-over-year price inflation rates over 8 percent and near 40-year highs.

Moreover, in its summary of economic projections, many FOMC committee members said they expected the target policy rate to reach or exceed 4.25 percent this year, and exceed 4.5 percent in 2023. Projections of economic conditions, however, continued to be relatively rosy with the report suggesting that GDP growth will stay above zero for the foreseeable future while unemployment maxes out at only 5 percent.
In spite of two quarters in a row of shrinking GDP over the past year, and in spite of many indicators of brewing recession—such as falling home prices and an inverting yield curve—the committee is still clinging to the idea that the Fed can steer a "soft landing" in which inflation will be reined in with no more than some moderate slowing in economic growth.
Although the recent hikes in the target fed funds rate suggest an increasingly hawkish position, the Fed nonetheless continues to take only the most tepid steps when it comes to reducing the size of the Fed's portfolio. Such a move would directly reduce the money supply by reversing QE, and it would also reduce asset prices by producing a small deluge of government bonds and mortgage-backed securities flowing back into the market.
While the Fed is allowing some government bonds to continue to roll off the portfolio, we shouldn't expect any drastic moves here. It's been nearly four months since the Fed announced plans to reduce the portfolio, yet the actual reduction continues to be miniscule. Moreover, in Powell's press conference on Wednesday, when asked about selling off the Fed's mortgage-backed securities, Powell responded "It's something I think we will turn to, but that time — the time for turning to it has not come ... It's not close."
Even now, after immense and rapid price inflation over the past two years, the Fed is still too afraid of fragility in the housing market to put much of its $2 trillion MBS portfolio back into the private sector.
This sends a mixed message as to how much the Fed is really committed to reducing price inflation, but it's clear Powell was trying to project a hawkish tone on Wednesday overall.
Powell spoke of "significantly reducing the size of our balance sheet" and also emphasized that ending the current bout of inflation will require pain in the form of job losses. He also emphasized that there is no short-term solution, strongly implying that the current effort to end inflation could possibly take years.
Powell expressed fears that price inflation will become much harder to address once the population comes to expect inflation as routine. He also noted that price inflation in housing "is going to remain high for some time." Powell then reiterated that there is no way to "wish away" inflation, but that the only way he sees the Fed can do something about inflation is by "slow[ing] the economy." (See 1:35:00 here.)
The question remains, however, as to whether or not the Fed and the federal government can politically tolerate a sizable period of rising interest rates and a decline in the monetary growth rate.
A decline in the monetary growth rate is trouble because it points to recession. Our bubble economy is now so addicted to easy money, that even a slowing in monetary expansion can send the economy's many zombie companies into a tailspin. Rising rates are a problem because they can lead to sizable increase in the federal government's debt-service payments. This could lead to a fiscal crisis without cuts to popular government spending programs. Virtually no one in Washington wants that.
Some key warning signs are already flashing "recession," such as the inverting yield curve. For example, the 10-year yield minus the 2-year yield has been negative since July, and at the most negative level since the early 1980s.


